Industrial hemp has been scientifically proven to absorb more CO2 per hectare during its growth cycle than any forest or commercial crop.
This means that the production of Hemp is carbon negative. It absorbs more carbon from the atmosphere during its growth than is emitted by the equipment used to harvest, process and transport it.
In addition, the CO2 is permanently bonded within hemp fibres that can go on to be used for anything from textiles to paper to building material (it is currently being used by BMW in Germany to replace plastics in car construction.)
As an alternative to what can be grown or sourced from oil, and given that it can be constantly replanted, it meets the permanence criteria as defined by the Kyoto Protocol.
So, what’s the science behind carbon capture?

One hectare of industrial hemp can absorb 22 tonnes of CO2. Where two crops per year are grown, absorption is doubled. And hemp’s rapid growth (up to 4 metres in 100 days) makes it one of the fastest CO2-to-biomass conversion tools available. Even more efficient than agro-forestry.
Biomass is produced by the photosynthetic conversion of atmospheric carbon, and the following carbon uptake estimates are calculated by the examining the carbon content of the molecules that make up the fibres of the hemp stem. Industrial hemp stem consists primarily of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin.
- Cellulose is 70% of stem dry weight. Cellulose is a homogeneous linear polymer constructed of repeating glucose units. The carbon content of cellulose accounts for 45% of its molecular mass.
- Hemicellulose is 22% of stem dry weight. Hemicellulose provides a linkage between cellulose & lignin. It has a branched structure consisting of various pentose sugars.
- Lignin is 6% of stem dry weight. Lignin is a strengthening material usually located between the cellulose microfibrils. The lignin molecule has a complex structure that is probably always is variable.
So to summarise the above, one tonne of harvested stem contains:
- 0.7 tonnes of cellulose (45% Carbon)
- 0.22 tonnes of hemicellulose (48% Carbon
- 0.06 tonnes of lignin (40% Carbon)
The roots and leaf mulch (not including the hard to measure fibrous root material) left in situ, represent approximately 20% of the mass of the harvested material in initial field trials. The resulting carbon content absorbed but remaining in the soil, will therefore be approximately 0.084 tonnes per tonne of harvested material.
As a low fertiliser and zero pesticide/herbicide crop, with little management input, the carbon emissions of hemp cultivation is well below the average. Therefore we can assume the matter remaining in soils roughly offsets the cultivation and management emissions.
The science is clear. The cultivation of industrial hemp is vital in our battle to reduce carbon, reduce pollution, conserve water and improve soil quality. Join us in making things better.
https://thailandhempfarms.com/
HEALTHY FOR THE PLANET
Global warming is in part due to the industrialized farming of animals for protein. Hemp seed provides more protein per gram than beef, more omega 3 and 6 than salmon and it captures carbon while doing it. In fact, it captures more carbon than any other crop during its growth cycle.
So hemp nourishes you thoroughly, oxygenates our atmosphere and benefits Thai farmers. That alone is extraordinary, but there’s more. Hemp requires no pesticides or herbicides (that’s right, the non-organic version too), so nothing is destroyed or poisoned in its production. It can grow just about anywhere, and it needs far less water than wheat, rice or soy.

HEALTHY FOR YOU
Hemp seeds are nature’s superfoods. Whether hulled or whole, they give you omegas 3, 6 and 9, protein, calcium, iron, phosphorous, magnesium, antioxidants, potassium and plenty of protein. They are also anti-inflammatory, high in digestible fibre, gluten free, lectin free and keto friendly.
Hemp protein powder is the richest, natural source of plant-based protein available, containing all 9 essential amino acids, without any of the phytic acid in soya. This means all its nutrients are easily absorbed and explains its popularity amongst athletes.
Hemp seed oil is high in GLA fatty acids, otherwise knowns as omegas 3, 6 and 9, in exactly the right proportions for your body. These wonder elements reduce cholesterol, keep your brain healthy and your hormones balanced. Then there’s hemp flour, which is low GI, low sodium, high protein and high fibre, plus it contains omegas 3, 6 and 9. It’s easily digested and perfect for those who have nut, gluten or wheat allergies.
Hemp vs cotton

Most cotton is GM. (Genetically Modified) Growing it uses 50% of the world’s agricultural water, 25% of all pesticides and herbicides which poison the soil.
It accounts for the vast majority of all fibre production and is only cultivable in subtropical climates. This limits the area of production and increases water requirements.
Hemp is a low maintenance crop, being a fast growing and much more hardy plant. It grows readily in most temperate or subtropical climates and is even capable of growing in climates ranging from Nepalese mountains to the equator. It typically requires no pesticides or herbicides. Productivity is over twice as high, with yields of up to 3 tonnes of dry fibre per hectare compared to 1.35 tonnes of cotton lint per hectare.
The high tensile strength of its individual fibres make hemp the strongest natural fibre apart from spiders’ silk. Hemp clothes are four times stronger than cotton and can make everything from light t-shirts to durable heavy canvas. Why aren’t we rethinking our textile industry?
Hemp vs Wood Based Paper

The pulp and paper industry is the 3rd largest industrial polluter. This is due to many factors including transport, energy use (fifth largest industrial consumer of energy in Europe) and chlorine based bleaches (three million tonnes) which enter the water supply. Paper production uses more water to produce a ton of product than any other industry and it produces almost 32 million tonnes of CO2 in Europe and 120 billion tonnes worldwide every year.
Today, 99.95% of paper and card comes from trees, but this was not always the case. Up until 1883, 75-90% of all paper in the world was made with hemp fibre. Deforestation is a global problem with approximately 80% of the world’s forests already destroyed, and paper production accounting for 35% of all felled trees.
The main advantage of hemp is its growth cycle. Hemp can grow up to 15 feet high within three to four months, whereas trees take at least 10 years to produce, per hectare, a comparative amount of pulp for paper. Cellulose is the principal ingredient in paper. Trees are only 30% cellulose, requiring the use of toxic chemicals to remove the other 70% of plant matter. Hemp contains up to 85% cellulose.
Hemp has a lower lignin content than wood at 5-24%. Wood has 20-35% lignin. Given lignin must be removed from the pulp before it can be processed into paper, using hemp means less power consumption and fewer chemicals. And chlorine bleaches can be replaced with non-toxic hydrogen peroxide when processing hemp. If we replace wood with hemp, we could grow our own packaging and paper industry here in Thailand– and save the trees.
Hemp vs the Oil Industry

Hemp is the most cost-efficient and valuable of all the fuel crops we could grow – and on a scale that could fuel the world. Hemp biodiesel can be made from domestically produced hemp oil and hemp ethanol can be made from fermented stalks. These fuels could be the answer to our increasing need for renewable fuel sources.
It’s nothing new. The concept of using vegetable oil as engine fuel dates back to 1895 when Dr. Rudolf Diesel developed the first diesel engine to run on vegetable oil.
Even Henry Ford built his first cars to run on bio-diesel. Imagine growing our own carbon zero fuel here in Thailand instead of importing high carbon fossil fuels.
Hemp vs Building Materials
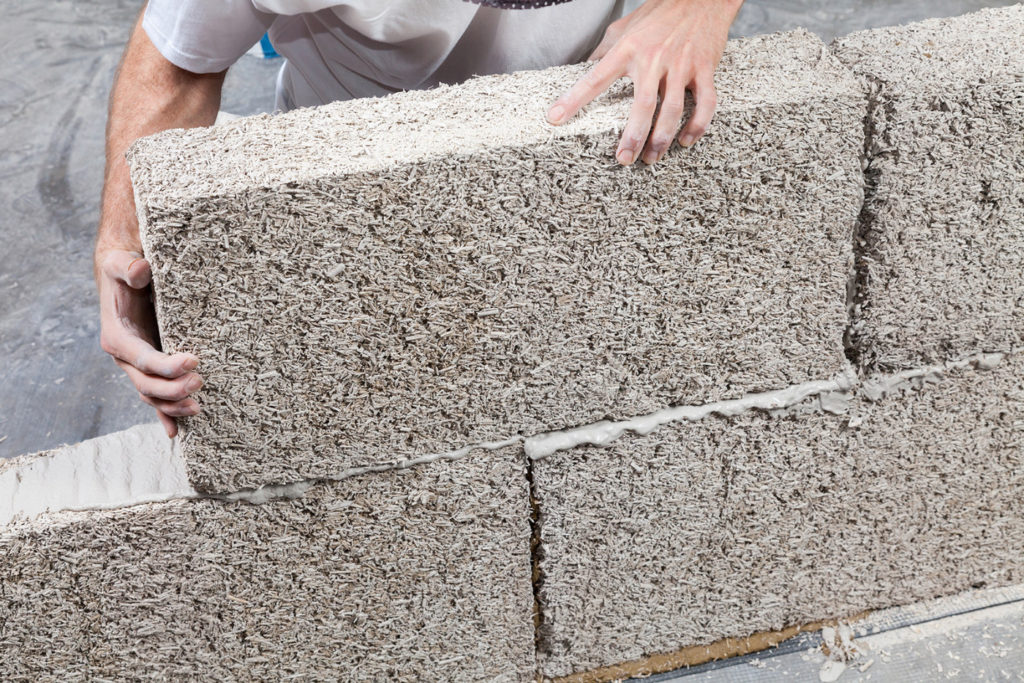

Hempcrete is a better-than-zero-carbon material. It’s carbon negative thanks to the amount of atmospheric carbon that is locked away for the lifetime of the building. And it’s not just hempcrete. A whole range of sustainable building materials are currently being made from the stalk of the hemp plant for use in restoration and new build projects:
Hemp fibre can also be made into recyclable loft insulation, with no contain harmful ingredients. Compressed hemp shiv (the woody inner portion of the hemp
stalk) is used to make a fibre board and a hardwood replacement. Hemp can even be used as a replacement for plastics and fibre glass in the construction industry. Why wouldn’t we grow our construction materials instead of relying on toxic imports?
Carbon footprint: a phrase we hear almost as often as we hear global warming and climate change. Not surprising, as all of them are connected. Climate change is a threat to the future of planet earth. Global warming is one of the major factors behind climate change. Increased carbon emission is one of the core reasons for global warming. In this article, we will discuss how hemp can help us reduce carbon dioxide and fight against global warming.
Carbon here refers to gas carbon dioxide or CO2. Human activities since the industrial revolution, and especially since the mid-20th century, has been consistently increasing the level of CO2 released into the earth’s surface. Hence the phrase ‘carbon footprint’. Today, the amount of CO2 in the earth’s atmosphere is much higher than what it would be naturally.
CO2 and the Greenhouse Effect
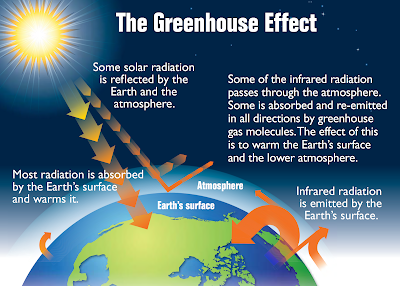
Higher levels of CO2 and some other gases in the earth’s atmosphere cause the greenhouse effect. A greenhouse is a structure built entirely of glass, used in gardening to grow plants that need warm weather. The typical use of greenhouses is for growing tropical flowers, fruits, and vegetables in places where the natural weather is cooler than these plants need.
A greenhouse maintains warmth 24X7 even during winter. The sunlight passes through the glass structure easily and warms the air inside during the day. The glass walls and ceilings trap the heat so that the warmth lingers through the night also.
Higher CO2 levels in the atmosphere have just this effect on the earth. CO2 traps the heat and increases temperature levels on the earth’s surface. It is like the whole planet is inside a greenhouse.
Why Does It Matter?
The current atmospheric CO2 level is higher than it has ever been in the last 800,000 years. In 2018, the CO2 level on the earth’s surface reached 407.4 parts per million, a record high after three million years.
Unless we control the greenhouse effect on the earth’s atmosphere, CO2 levels are likely to cross 900 parts per million by the end of the 21st century. Higher levels of thermal energy trapped on the earth’s surface imply that the planet is warmer than it would be naturally.
So what if we live in a warmer planet? Well, for one, it causes the polar ice to melt faster than it gets replaced. The Arctic and Antarctic icecaps play a critical role in keeping our landmass intact. If these icecaps get damaged, all coastal areas in the world will be submerged.
Ocean and sea levels are rising because of global warming. That is another threat to losing coastal areas to water bodies. Also, the natural habitat of flora and fauna gets affected and so does the overall ecological balance. Also, our oceans are already 30% more acidic because of absorbing excessive CO2.
The threats are many and varied. One way out is to explore outer space for creating new human settlements there. But a much more practical solution is to look for natural responses to reduce the greenhouse effect.
Why Hemp Counts

The hemp, or industrial hemp as it is also called, the plant is a natural solution to much of the excessive CO2 emission issue. It is an amazingly versatile plant that had been in human use for thousands of years. It is only in the 20th century that we declared it an outlawed plant in many countries of the world.
A simple act of omission caused this (though there are conspiracy theorists who believe that it was more an act of commission). Psychoactive cannabis or marijuana is a cousin of the hemp. They both belong to the same plant species, Cannabis Sativa. But hemp does not have the psychoactive properties of its cannabis cousin.
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the chemical that gives marijuana its capacity to cause a “high”. But the THC level in the industrial hemp is limited to 0.3%. That is why this plant does not have the psychoactive capacity of cannabis the drug.
Hemp has a number of benefits for human beings and the environment we live in. Reducing our carbon footprint is only one of them. Hemp offers Mankind a way to change almost everything we do!
Fossil Fuels vs. Hemp Biofuel
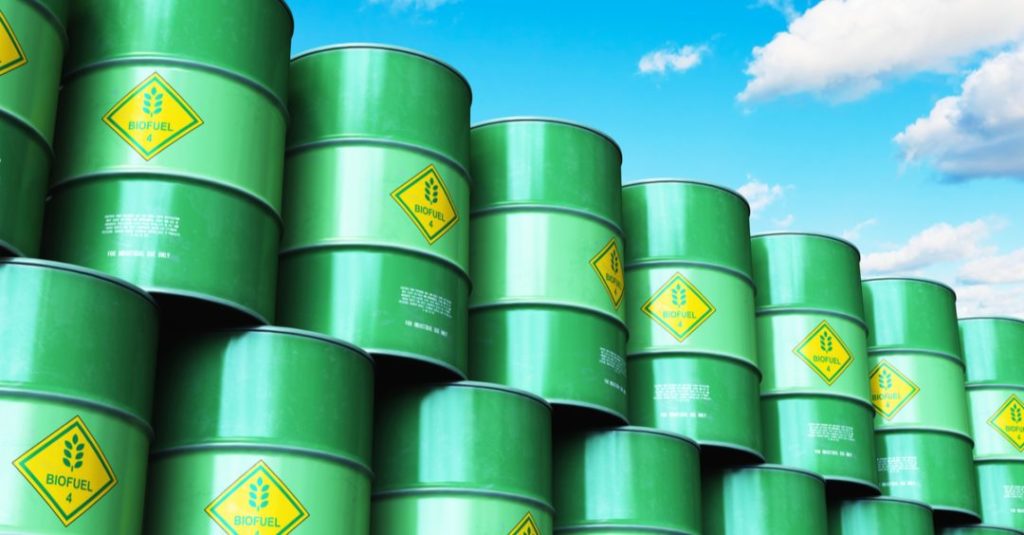

Much of the excess CO2 in the earth’s atmosphere is because of our dependence on fossil fuels like petrol and diesel. Hemp biofuel is one of the most easily available renewable energy sources that we can use to substitute fossil fuels.
Industrial hemp is a feasible source of producing bio-diesel.
One of the main advantages of using hemp for producing biodiesel is that the plant grows on infertile soil not suitable for cultivating other crops, especially foodgrains. It is an easy-to-grow plant that needs no additional fertilizers and is naturally resistant to pests.
The research report states that hemp seeds are naturally rich in oil content and 97% of that can be used to generate biodiesel. Hemp biofuel can also be used at temperatures lower than other plant-based fuels presently in use.
Hemp Can reduce Carbon Dioxide

Planting more trees is an effective means of addressing the carbon emission issue, for plants absorb carbon dioxide. Hemp is a plant with a particularly high level of efficiency in this regard. Experts say that every ton of hemp can sequester 1.62 tons of CO2. In simple language, that is how much CO2 a ton of hemp can trap and hold.
Hemp can also reintegrate CO2 back into the soil through biosequestration. This is a process of smoldering a harvested plant slowly. Harvested hemp produces charcoal-like biochar when smoldered slowly post-harvest. To mix this biochar with the soil is to return the carbon to the soil, rather than releasing it into the atmosphere.
Hempcrete Reduces Carbon Emission
A recent report from the United Nations Environment Program mentions that the construction industry is responsible for up to 30% of the total greenhouse gas emissions globally. This industry also accounts for about 40% of the total global energy consumption.

Using hempcrete as insulation for buildings can reduce carbon dioxide emissions considerably. One square meter of a hempcrete wall framed by timber can store up to 35.5 kg of CO2. That is after absorbing the energy cost of transportation and assembling of the materials.
Hempcrete is a biocomposite made of hemp hubs, water, and lime or some other natural binder. Hemp hubs or shives are the inner core of hemp stalks left after the outer fibers have been taken out. These hubs are woody in texture. Hempcrete is not strong enough for load-bearing, but they are effective for insulation.
Hempcrete insulation also reduces energy consumption for insulating buildings as it is naturally breathable. It can both store thermal energy and release it, which makes it suitable for different temperature zones.
Think Hemp for a Greener Planet
There are myriad other ways that hemp can help us find natural solutions to the climate change menace. Reducing our carbon footprint is only one of them. It is time we started relying more on the ancient wisdom associated with the use of this miracle plant.
We are often very complacent in matters where we are not impacted directly, immediately or when the effect is slow, though the result is going to be catastrophic. We have ruined our planet with our so called intelligence and modern lifestyle. We don’t have enough trees on the planet, we have ruined marine life, we are filling our bodies with chemicals, micro plastics , and call ourselves modern.
It’s time that we all rise to the looming environmental catastrophe and choose wisely. Don’t choose fast fashion. Don’t use products which cut trees, plant more trees, choose organic food and smile a lot. I am the CEO & Founder at Hemp Foundation and I urge us to not take the above words lightly.
Act now, Act from today. For your children, for the planet, for your loved ones. I personally feel that Hemp can help us fight a lot of our above problems. Please read about it and if you like, use as much hemp products as possible.
Hemp is currently being “Discovered by our Thai Government as it is being discovered, AGAIN, all around the World. Hemp was before used in everything.
The Last thing the two Largest Lobbyist ( Petroleum and Pharmaceutical) in our Country want you doing is going to the Store and Buying some Rope made from Hemp or going to your Back Yard and gathering Medicine (Cannabis) vs using your car, spending money on Petroleum to go to the Pharmacy and Purchase a synthetic Drug for relief. Everyone has Dirt, Sunlight and Water!! Cannabis Likes these things.
For Example: Back in “The Day” all rope in the World was made from Hemp. Then Nylon was discovered…Time to move back to “The day”. Economics, Destruction is one way to have our Governments take notice. You can also direct your “spending” towards a sustainable style of Living.
Regards!
Kevin Leopard
Grower/CEO
Thailand Hemp Farms https://thailandhempfarms.com



0 Comments