Every Human Body has an EndoCannabinoid System. This is Largely why Cannabis is being recognized now. Cannabis contains all sorts of “Cannabinoids”
When our bodies are in a state of balance, they are naturally pain free, relaxed, and restorative. However, what exactly happens when our bodies experience pain?
We don’t want to eradicate inflammation as that is impossible and it is a natural immune response meant to help our bodies fight infections, viruses, and more. When small microbes or mucus droplets enter our system, our bodies cannot recognize what they are or where they come from, so they naturally trigger immune cells to create inflammation. This is something I never understood, why are mask enforced, yet Eye Protection is not. If a “droplet” lands in your eye, a person can catch Covid just as easily.
Inflammation leads to more blood flow in an area allowing immune cells to enter and try to heal the wound or get rid of foreign invaders. It also creates a hostile environment where certain germs would not want to live in.
While occasional swelling is normal, people with chronic illnesses often experience chronic swelling that puts the body in a state of stress. This swelling leads to extra sensitivity to pain and chronic feelings of pain as well.
So, how can we reduce inflammation, increase pain relief, and bring the body back to balance?
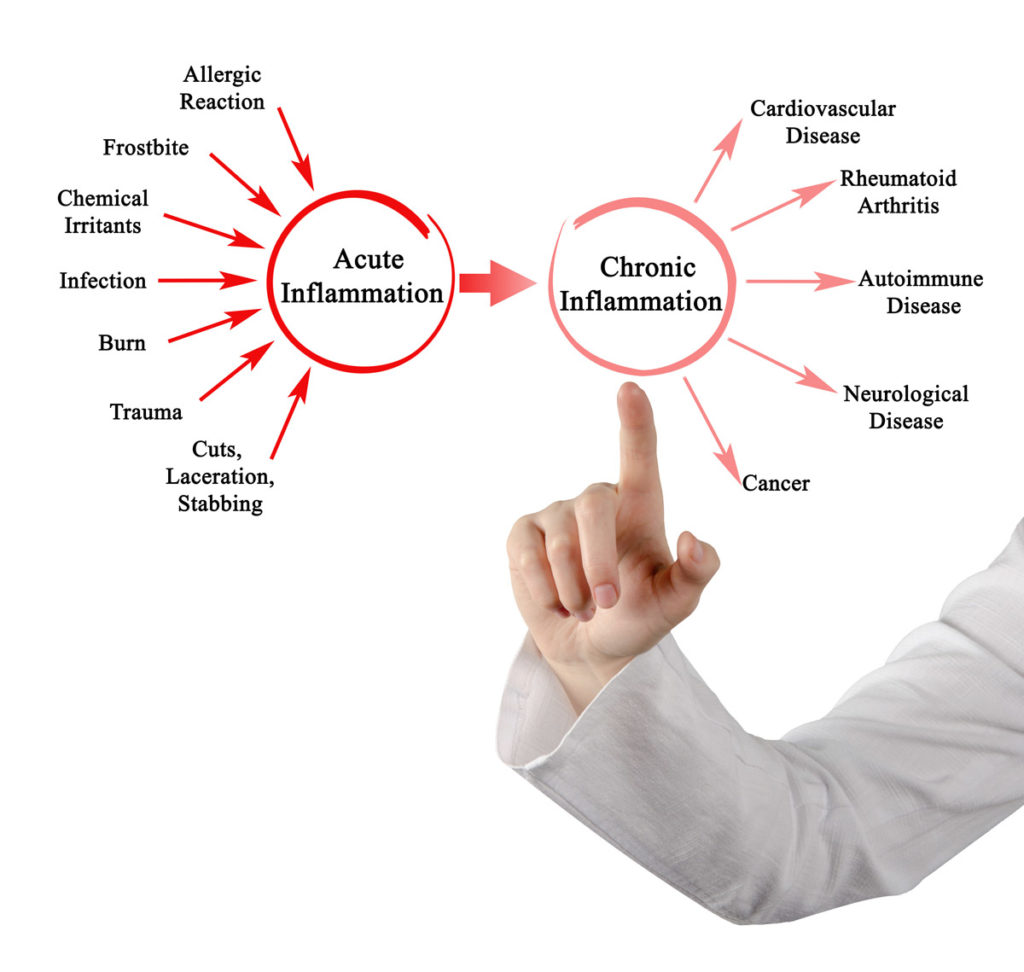
While there are many factors that affect our bodies’ inflammation response and level (i.e., genetics, diet, exercise, allergies, etc.), there are certain FDA approved medications and other natural alternatives that may help.
Chronic pain and inflammation often related to an autoimmune disease are usually treated with corticosteroids (a prescription drug), or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), but these can negatively affect hormones, mood, weight, liver function, and may even cause stomach ulcers.
There are natural alternatives that may relieve pain, have little side effects, and may help manage certain health conditions.
The Cannabis plant has been highly regarded for its natural analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. Cannabidiol, CBD, a molecule found within this plant, has been highlighted for its potential ability to reduce inflammation and thus reduce pain.
CBD, THC, CBN, and other molecules of the Hemp plant are known as Cannabinoids. While our bodies produce their own Cannabinoids, we sometimes don’t produce enough which can lead to issues within. CBD helps mimic a response that comes from our own internal system to help compensate.
Unlike other systems in our bodies, the Endocannabinoid system (ECS) was not discovered until 1992. This is why CBD and its effects have only started being researched recently.
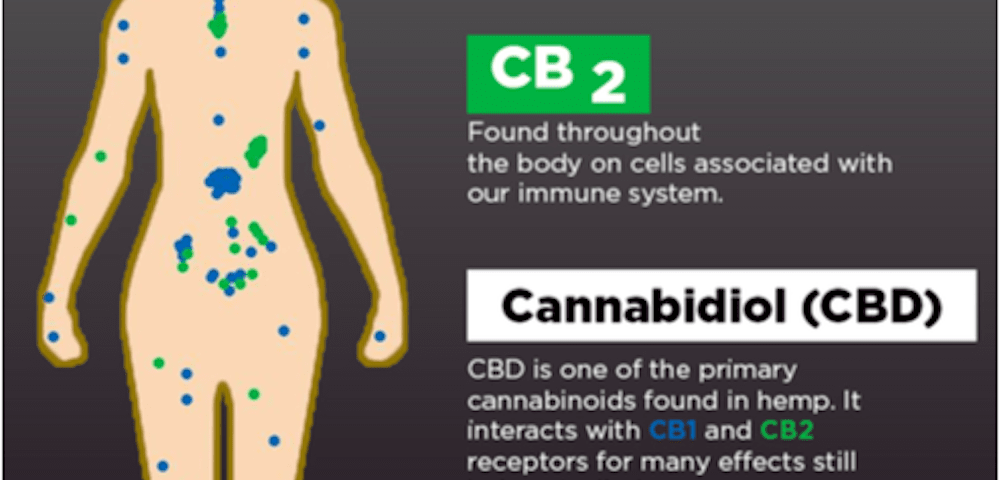
While the effects of CBD are still being studied, the majority of research demonstrates that CBD oil can be effective at targeting pain and inflammation. This is attributed to the fact that we all have an internal system responsible for producing biological Endocannabinoids and managing organ function, pain regulation, appetite, mood, and more.
Above all, though, CBD’s main target is that of immune and pain response which explains its ability to de-swell the body! CBD products help you de-stress, relieve pain, and de-swell.
Thailand Hemp Farms Produces Hemp with the Highest Levels of CBD/Cannabinoids, Terpenes and Flavonoids available in Thailand.
What are Flavonoids?
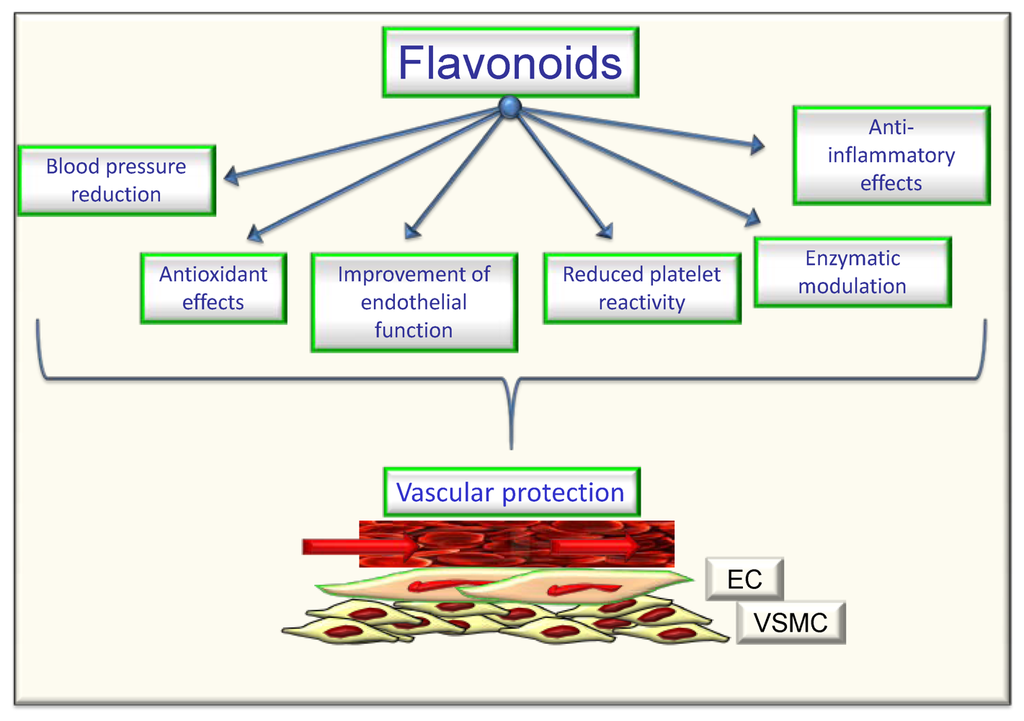
There has been increasing interest in the research of Flavonoids from dietary sources, due to growing evidence of the versatile health benefits of Flavonoids through epidemiological studies. As occurrence of Flavonoids is directly associated with human daily dietary intake of antioxidants, it is important to evaluate flavonoid sources in food. Fruits and vegetables are the main dietary sources of Flavonoids for humans, along with tea and wine.
However, there is still difficulty in accurately measuring the daily intake of Flavonoids because of the complexity of existence of Flavonoids from various food sources, the diversity of dietary culture, and the occurrence of a large amount of Flavonoids itself in nature. Nevertheless, research on the health aspects of Flavonoids for humans is expanding rapidly.
Many Flavonoids are shown to have antioxidative activity, free-radical scavenging capacity, coronary heart disease prevention, and anticancer activity, while some Flavonoids exhibit potential for anti-human immunodeficiency virus functions. As such research progresses. further achievements will undoubtedly lead to a new era of Flavonoids in either foods or pharmaceutical supplements.
Accordingly, an appropriate model for a precise assessment of intake of Flavonoids needs to be developed. Most recent research has focused on the health aspects of Flavonoids from food sources for humans. This paper reviews the current advances in Flavonoids in food, with emphasis on health aspects on the basis of the published literature, which may provide some guidance for researchers in further investigations and for industries in developing practical health agents.
What are Terpenes?
If you have ever had a waft of particularly aromatic plants such as Lavender, you’ve encountered Terpenes. Terpenes are aromatic compounds that create the distinct scent of many plants like Cannabis, Pine, Lavender, and Oranges.
However, creating the aroma of Hemp and other plants is not the only purpose of these important chemicals. Terpenes serve a protective function for the plant and may also offer some health benefits to the human body.
Read on to find out more about the benefits of Terpenes in CBD.
What are Terpenes?

Terpenes are fragrant organic compounds found in hemp and other plants that bind to receptors in the Human body and carry a variety of health benefits.* Terpenes are responsible for the aroma and flavors of some Hemp-derived CBD products, having effects by interacting with cannabinoids.
Hemp-derived terpenes are formed inside Cannabis Trichomes, and their relative presence is directly affected by both the spectrum and intensity of light exposure. Terpene profiles vary amongst Hemp plants, influencing their unique aroma profiles. Different Hemp plants will produce distinct scents based on their unique blend of terpenes.
Why Do Plants Produce Terpenes?
In some Plants, Terpenes act as a way to attract pollinators or repel predators, such as insects or foraging animals. Terpenes also play a protective role, helping the plant to recover from damage, while others act as a part of the plant’s immune system to keep away harmful germs.
Types of Terpenes
There are many distinct types of Terpenes, each with a unique aroma profile and purpose. Some of the most common terpenes found in Hemp are:
- Caryophyllene– A terpene in hemp, caryophyllene is also found in hops, cloves, and rosemary. It carries an herbal aroma synonymous with these plants.
- alpha – Humulene– This terpene is dominant in hops. It’s also present in sage, clove, basil, black pepper, and ginseng, and carries a corresponding “hoppy” aroma.
- Limonene– Most commonly found in citrus fruits, in which it provides that citrus smell.
- Linalool– This terpene is found in rosewood, bergamot, coriander, rose, jasmine, and lavender. It produces a very pleasant floral aroma and is often used in soaps and perfumes.
- Myrcene– Most commonly associated with the signature “earthy” aroma found in most hemp plants.
- Ocimene– Produces a strong, sweet, herbal scent. wide variety of plant life, including mint, mangoes, basil, and orchids.
- Pinene– Similar to its name, it is commonly found in pine trees and other conifers, pinene is also responsible for the “piney” aroma of certain hemp plants.
- Terpinolene– It’s commonly found in plants known for pleasant fragrances, such as rosemary, conifers, lilacs, and apples. It creates a fresh herbal-citrus aroma.
- alpha Bisabolol– This terpene was first isolated from Matricaria chamomilla (Asteraceae) in the twentieth century and has since been identified in other aromatic plants such as Eremanthus erythropappus, Smyrniopsis aucheri, Vanillosmopsis species, and Salvia runcinata.


